What is a Linked List ?
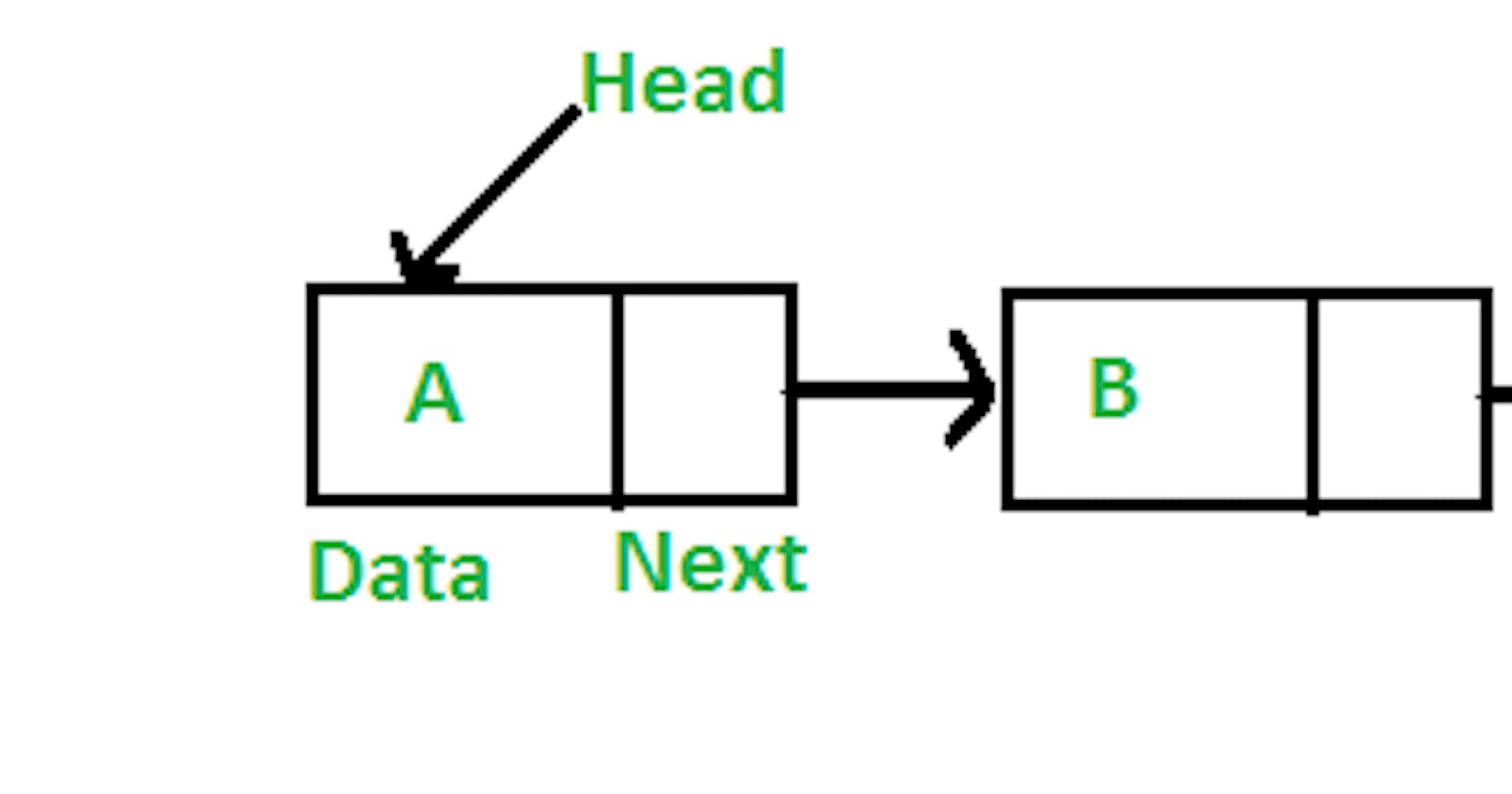
A linked list can be visualized as below:
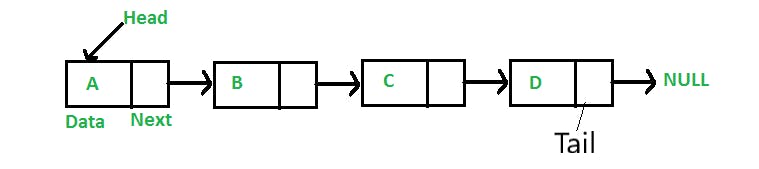
If you look at the image provided above:
- You can see there are 4 Nodes (or cell), each with a partition in it:
- The first partition represents data (A, B, C or you could store numbers [1,2,3] in them)
- The second partition represents a pointer (next) to the next node/cell
- A Linked List is just a sequence of these Nodes
- The beginning Node of the Linked Lists is called a Head and the End Node of the linked list is called Tail
Python Code (We will be adding nodes, deleting nodes and printing the LinkedList):
# This is Node/Cell of a Linked List
# We will use this to create a new Node/Cell within the Linked List class below
# addToHead (add Node to beginning) and addToTail (add node to end) will use the Node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def addToHead(self, data):
# Convert the provided data to a Node
newData = Node(data)
# Connect the newData node to pre-existing LinkedList
newData.next = self.head
self.head = newData
def printLinkedList(self):
# pointer to the Linked List as we want to parse through the entire LinkedList
# and do not want to edit the linked list itself (hence don't directly use self.head)
cur = self.head
print('Printing...')
while cur:
print(cur.data)
# move to the next node of LinkedList after printing the cur LinkedList node
cur = cur.next
def addToTail(self, data):
newData = Node(data)
cur = self.head
# stop right before cur reach end (i.e: None)
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = newData
def deleteNode(self, data):
# prev will be used once cur reaches the Node/data to skip over the cur Node/element
prev = None
cur = self.head
while cur:
if cur.data == data:
break
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
# if first Node is the data to be deleted then just move head to next Node
if prev == None:
self.head = self.head.next
else:
# skip over cur element
prev.next = cur.next
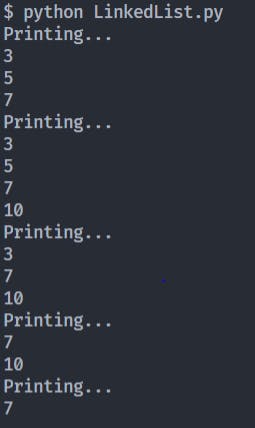
Alright now that we have our LinkedList data structure created, lets call and create our LinkedList:
# Initiliaze an empty Linked list i.e: self.head = None
ll = LinkedList()
ll.addToHead(7)
ll.addToHead(5)
ll.addToHead(3)
ll.printLinkedList()
ll.addToTail(10)
ll.printLinkedList()
ll.deleteNode(5)
ll.printLinkedList()
ll.deleteNode(3)
ll.printLinkedList()
ll.deleteNode(10)
ll.printLinkedList()
And the Output should look like this for the above calls: