BubbleSort uses nested for loops in order to sort an array and therefore has a time complexity of O(n^2). That is slow, but it is still an important algorithm to know.
How it works:
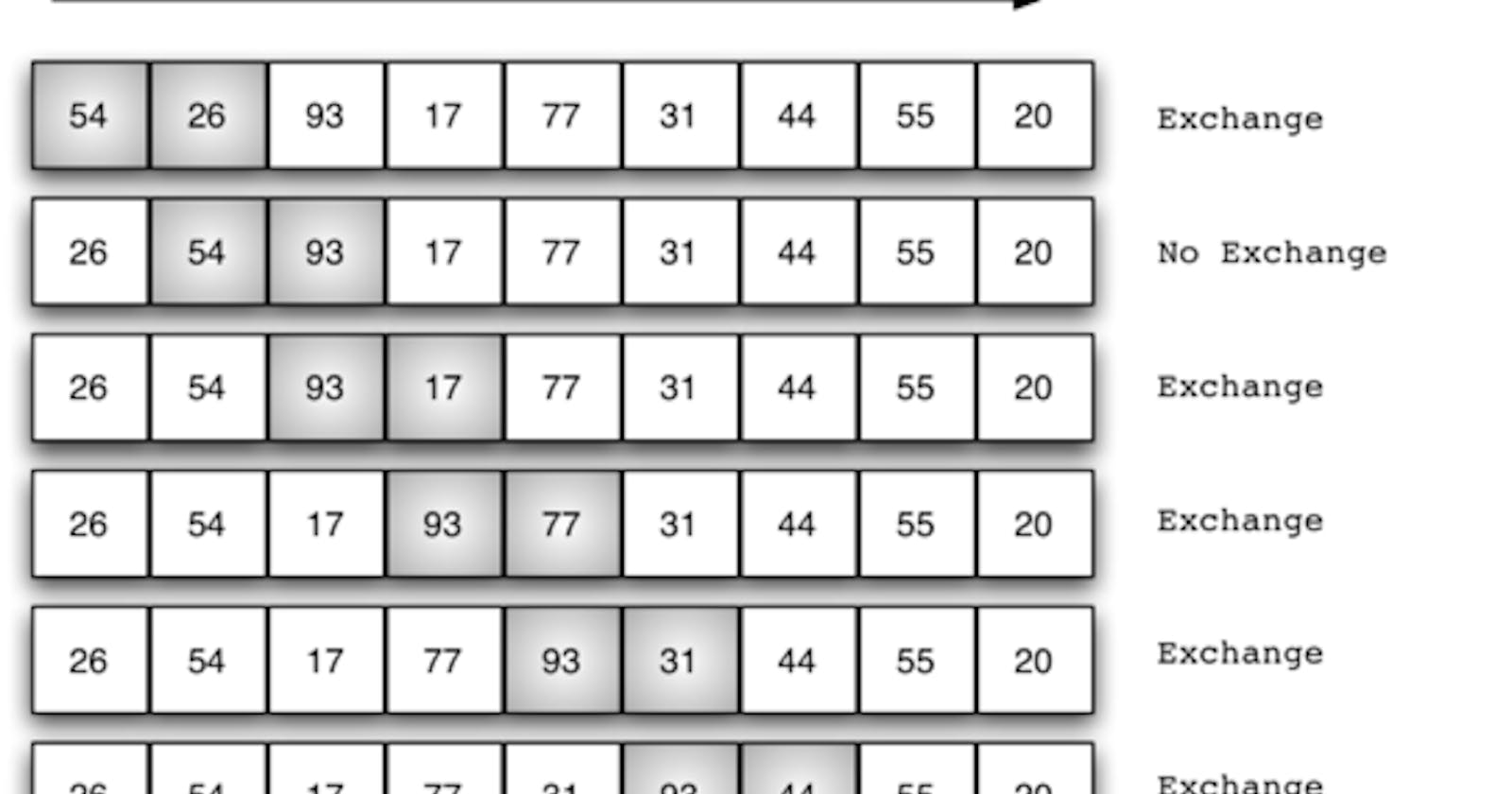
Take array, arr = [54, 26, 93, 17, 77, 31, 44, 55, 20] size, n = 9
BubbleSort compares two adjacent elements and the larger value is put to the right/bigger index.
eg: arr[0] = 54 and arr[1] = 26 since arr[0] > arr[1] we will put the larger value to the right or bigger index i.e.: arr[1] = 54 and arr[0] = 26
If we use the above logic and iterate through the entire array once, we will have the largest value in the array placed at the end:
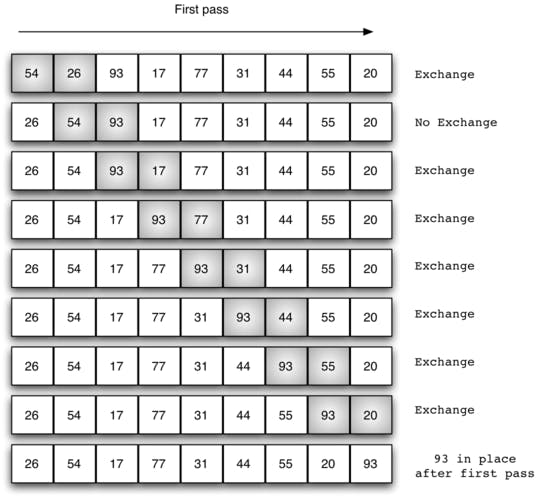
Now, that we have the largest element at the end we can ignore the last element of the array and apply the same logic to arr n-1, n-2, n-3, ..., 1, 0; This can be achieved using the nested/outer for loop on the array.
Algorithm:
def bubbleSort(arr):
# variable i will be used to decrease the array iterated through
# by the inner for loop by size 1 (n-1, n-2, n-3 ... 0);
# since after each iteration of the inner for loop the largest element is at the last index
# and thereby in the correct sorted index.
for i in range(len(arr)):
# len(arr)-i = 9 (9-0), 8(9-1), 7(9-2), ... 0 (9-9)
# The -1 value is used since we will be comparing i with i+1 and that
# could lead to index out of range error
for i in range((len(arr)-i)-1):
# check if smaller index i is larger than bigger index i+1
if arr[i] > arr[i+1]:
# save arr[i] value in temp, overwrite arr[i+1] value to arr[i] and then replace arr[i+1] with larger temp/arr[i] value
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[i+1]
arr[i+1] = temp
return arr
print(bubbleSort([54, 26, 93, 17, 77, 31, 44, 55, 20]))